enzymatic gravimetric method disadvantages|Determination of total dietary fibre and available : suppliers Enzymatic-gravimetric methods. In the early 1980s, a enzymatic-gravimetric method was developed in which the sum of soluble and insoluble polysaccharides and lignin were . Assista Gozando na buceta da morena em Portuguese em Pornhub.com, o melhor site pornô explícito. A Pornhub é o lar da maior e melhor coleção de Pornô em Portuguese.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB30 de ago. de 2023 · The Enigma of Fapello: Harmonizing Crazy Concepts with Pragmatic Execution. Infusing the unpredictability of Tim Burton with Vivienne Westwood’s rule .
Two general types of methods have been developed for isolating and analyzing dietary fiber: enzymatic-gravimetric and enzymatic-chemical. The food components isolated vary .Enzymatic-gravimetric methods. In the early 1980s, a enzymatic-gravimetric method was developed in which the sum of soluble and insoluble polysaccharides and lignin were .The AOAC method is an enzymatic- gravimetric procedure to determine the total dietary fibre (TDF). The Englyst method involves enzymatic-chemical extraction and fractionation of the . Enzymes employed had to meet specific activity requirements and be devoid of contaminating enzymes active on dietary fibre components. The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in .
This article highlights the lack of consensus on its chemical definition and the advantages and disadvantages of the two main methods used to measure it. These are the enzymic .187. The present summary will primarily deal with advantage and limitations of the enzymatic-gravimetric and enzymatic-chemical DF methods commonly in use. The enzymatic-chemical methods with gas-liquid chromatography (GLC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or colorimetry as endpoint determination are . What was clear from both reviews is that there is an immediate need to re-evaluate the methods that are used for dietary fibre measurement and to make appropriate changes .
The two main approaches for the determination of dietary fibre (DF) in food and feedstuffs are the enzymatic- and nonenzymatic-gravimetric AOAC (Association of Official Analytical .
The AOAC method is an enzymatic- gravimetric procedure to determine the total dietary fibre (TDF). The Englyst method involves enzymatic-chemical extraction and fractionation of the non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) and their subsequent determination as neutral sugars by GLC. The AOAC method gave a higher fibre value than the Englyst method due .It is for these reasons that gravimetric analysis is important. Disadvantages and Limitations. Gravimetrical methods have been a traditional and widely used technique in chemical analysis; however, they come with certain . A. Principle. The method measures IDF, SDF and TDF as defined by the CAC ().The method quantitates IDF and SDF which precipitates in 78% aqueous ethanol (SDFP) by gravimetric procedures, SDF which remains soluble in 78% aqueous ethanol (SDFS) by HPLC, and TDF by gravimetric and HPLC procedures (Figure 2022.01A).SDF is calculated by .The enzymatic-chemical methods with gas-liquid chromatography (GLC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or colorimetry as endpoint determination are generally more complex, involve more steps and require, for the GLC and HPLC methods, more advance equipment than the gravimetric procedures.
arrowheads geological hardness tests
This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant .
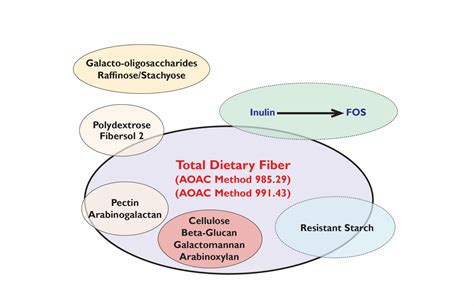
AOAC Official Methods SM 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, respectively). In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37 C to simulate human intestinal digestion followed by gravimetric isolation and quantitation of HMWDF andThis article highlights the lack of consensus on its chemical definition and the advantages and disadvantages of the two main methods used to measure it. These are the enzymic gravimetric method (AOAC) that measure fibre as the weight of residual matter following enzymic treatment of the food; and the enzymic chemical method that identifies and . The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in Foods; Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method’ 4, 5. Subsequently, the method was extended to allow measurement of total, soluble and insoluble dietary fibre in foods (AOAC Official Method 991.43) 6 , and various other modified methods for fibre determination have been .A method for the determination of total dietary fiber (TDF), as defined by the CODEX Alimentarius, was validated in foods. Based upon the principles of AOAC Official Methods 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, re .
Method 925.10 in Official Methods of Analysis, 18th Edition (AOAC International, 2007) provides an approved method for determining the moisture content of flour. A preweighed sample is heated for one hour in a 130 o C oven and transferred to a desiccator while it cools to room temperature.
The original AOAC enzymatic-gravimetric method for the determination of total dietary fibre (TDF) was developed on basis of the joint experience of Asp et al. (1992). The origins of these methods can be tracked back to the biochemical approach of measuring the indigestible residues in human foods introduced by AOAC 991.43 is an enzymatic-gravimetric method commonly used for measuring IDF, SDF, and TDF in foods . This method involves the enzymatic hydrolysis of starch and protein, followed by the precipitation of fibrous components by aqueous ethanol. The dietary fibre residues are then weighed, and the total dietary fibre content is calculated, using .Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method for estimating the quantity of a chemical correctly based on the mass of a solid.. Gravimetric analysis can be used in a variety of ways including the chemical analysis of ores and other industrial materials, equipment calibration, and elemental analysis of inorganic substances.. It is used to assess the chemical composition of rocks, .
Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method of measurement in chemistry. This measurement method is often used in analytical chemistry because of its high rates of precision and accuracy.Aluminum, Iron, Phosphorus, and Titanium Oxides in Liming Materials: Gravimetric Method Notes. Notes. 1.3.04 AOAC Official Method 917.02 Calcium in Liming Materials: Gravimetric Method Notes. Notes. 1.3.05 AOAC Official Method 919.01 Magnesium in Liming Materials: Gravimetric Method . Colorimetric Enzymatic Method Notes .
AOAC OFFICIAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS Supplement March 1995 32.1.17 AOAC Official Method 991.43 Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Dietary Fiber in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method, MES—TRIS Buffer First Action 1991 Final Action 1994 (Applicable to processed foods, grain and cereal products, fruits, and vegetables.) Method Performance:Gravimetric analysis is a method in analytical chemistry to determine the quantity of an analyte based on the mass of a solid. Example: Measuring the solids suspended in the water sample – Once a known volume of water is .
Enzymatic–Gravimetric Method Total dietary fiber should be determined on dried, low-fat, or fat-free sample. Homogenize sample and dry overnight in 70 °C vacuum oven. Cool in desiccator, reweigh, and record weight loss due to drying. Dry-mill portion of dried sample mesh.Enzymatic gravimetric methods date back to the 19th century. In the 1930s, McCance et al. measured total unavailable carbohydrates in fruits, nuts, and vegetables by determining the residue insoluble in 80% ethanol. This was corrected for starch measured after enzymatic hydrolysis with taka-diastase and for protein.Ask the Chatbot a Question Ask the Chatbot a Question gravimetric analysis, a method of quantitative chemical analysis in which the constituent sought is converted into a substance (of known composition) that can be separated from the sample and weighed. The steps commonly followed in gravimetric analysis are (1) preparation of a solution containing a known weight of .
DNA and Aspects of Molecular Biology. Eric T. Kool, in Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry, 1999 7.10.9.2.1 Enzymatic methods. The simplest enzymatic method for ligation of single-stranded circles is analogous to the method used for duplex DNAs. The difference here is that one uses a separate “splint” oligonucleotide to hybridize to the two reactive ends such that .The disadvantages of this method are (i) . Enzymatic Methods. Analytical methods based on enzymes rely on their ability to catalyze specific reactions. These methods are rapid, highly specific and sensitive to low concentrations and are therefore ideal for determination of carbohydrates in foods. . Gravimetric Methods. Crude Fiber Method . A broad range of AOAC official methods of analysis (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since the adoption of the Prosky method (OMA .
DOI: 10.1093/JAOAC/75.3.395 Corpus ID: 128658872; Determination of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fiber in foods: enzymatic-gravimetric method, MES-TRIS buffer: collaborative study ENZYMATIC-GRAVIMETRIC METHODS The original AOAC enzymatic-gravimetric method for the determination of total dietary fibre (TDF) was developed on basis of the joint experience of Asp et al. (1992). The origins of these methods can be tracked back to the biochemical approach of measuring the indigestible residues in human foods introduced by .
Enzymatic–Gravimetric Method Total dietary fiber should be determined on dried, low-fat, or fat-free sample. Homogenize sample and dry overnight in 70 °C vacuum oven. Cool in desiccator, reweigh, and record weight loss due to drying.Two methods (an AOAC and a simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method) were used to analyze seven types of canned legumes and eight cooked legumes. Total dietary fiber (TDF) of the canned products ranged between 17% and 23% (dry basis) for chick peas, Great Northern beans, kidney beans, pinto beans, pork & beans, vegetarian beans in tomato sauce .
asa 103 test hard
Methods for analysis of dietary fibre
Resultado da Hola mis amores Bienvenidos a mi mundo ☺😚INSTAGRAM - @isa.ramirezoficial TWITTER - @isaramirezreal
enzymatic gravimetric method disadvantages|Determination of total dietary fibre and available